VIDEOSTREAMING
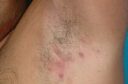
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), commonly known as “dog breast disease” is a condition characterized by the long-term inflammation of certain sweat glands. It typically occurs after adolescence. There are two types of sweat glands in our bodies; apocrine and eccrine sweat glands. HS is a disease that results from chronic inflammation of apocrine sweat glands, leading to the blockage of their ducts and the formation of abscesses beneath the skin due to this inflammation. These abscesses can later become fistulous, causing foul-smelling discharges. During the chronic inflammatory process, nodules can be detected under the skin, which eventually heal with fibrosis.
This disease mostly affects areas where apocrine sweat glands are located, such as the armpits, groin, perianal region, and the lower regions of the breast tissue. The prevalence of this condition ranges from 0.1% to 2%. It is more commonly seen in women, especially in the third and fourth decades of life, individuals of African descent, and the people who has lower socioeconomic status. Due to the reasons mentioned above, patients unfortunately tend to isolate themselves from social life. As a result, they may experience various psychological problems. Additionally, hospitalization and emergency department costs associated with HS can impose a significant financial burden on society.