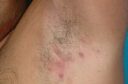
Hidradenitis Suppurativa is an inflammatory disease characterized by the accumulation and subsequent inflammation of the sweat gland as a result of the obstruction of the channels opening to the skin of the sweat glands, including the hair follicle.
The inflammation in this formed sweat gland then opens tunnels and spreads to other sweat glands and other tissues under the skin. Since it is an inflammatory disease, inflammatory and anti-inflammatory drugs have an effect in its treatment. These are anti-inflammatory drugs as well as antibiotics. In addition, some immunomodulatory drugs, which we call TNF-Alfa biokers, have also shown their effects in this disease.
However, an initiated Hidradenitis Suppurativa disease can never be cured completely with drugs. Because the inflammation does not completely disappear there. Healed areas heal with hydrosis, and an infection that started in areas with sweat glands and hair follicles can recur at short or long intervals. Here, real and complete treatment is only possible with surgery.
There are several forms of the surgical method: One of them is the methods that will drain the inflammation and relax the patient. With these -minor surgical procedures- inflammation is eliminated in the active period. But the definitive treatment is based on the method of completely removing the diseased area in that region and covering those areas with skin patches. When this entire inflammatory area is removed, the chance of recurrence of the disease in that area is zero. However, where there are sweat glands in other parts of the body, there is still a chance for the disease to arise. The thing to do here is to excise that area with minor surgical interventions as soon as the disease starts, so that people can return to their normal life.
As a result, there is a complete cure for Hidradenitis Suppurativa. The method for this is only surgery.